Start thinking more like an analyst.
Learn data science, natural language processing, and big data analysis essentials at your own pace.
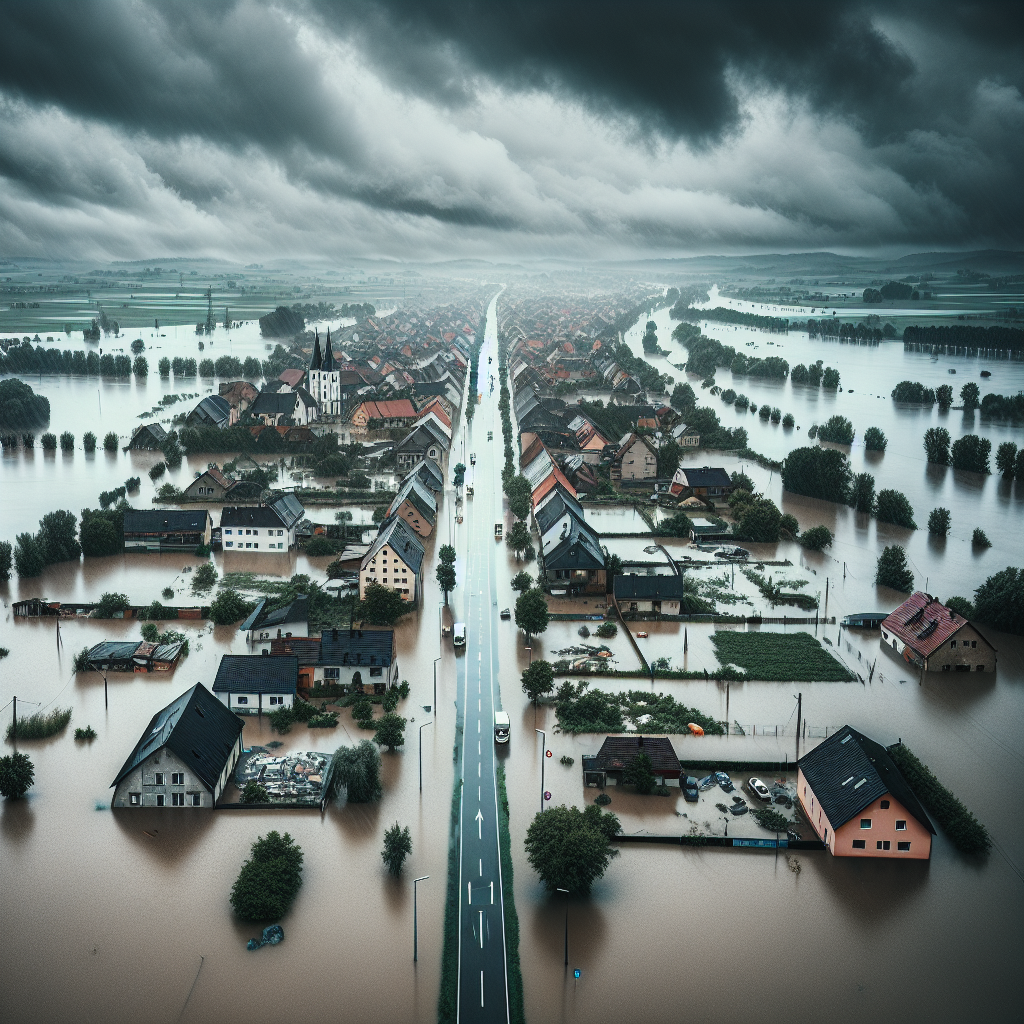
Human-Induced Climate Change Doubles Probability of Severe Rainfall and Flooding in Central Europe
A recent study by World Weather Attribution has revealed the shocking impact of human-induced climate change, suggesting that it has doubled the probability and intensity of heavy rains that have led to devastating floods in Central Europe. The study found that the torrential rain from Storm Boris in mid-September resulted in widespread damage across various Central European countries. The aftermath of the storm was catastrophic, claiming 24 lives, destroying critical infrastructure, and causing massive power outages. The unprecedented rainfall overwhelmed rivers and drainage systems, leading to rapid and uncontrollable flooding in both urban and rural areas. Emergency response teams were stretched to their limits, struggling to provide aid and evacuate residents from the most affected zones. The extensive damage to transportation networks, including roads and railways, further hampered rescue and relief operations, illustrating the far-reaching consequences of such natural disasters.
The study pointed out that human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, have contributed significantly to climate change, making the severe four-day rainfall twice as probable and between 7% and 20% more intense. The researchers utilized climate models to analyze the impact of human-induced climate change, comparing how these events have evolved since pre-industrial times. These models showed a clear trend of increasing rainfall intensity and frequency, correlating directly with rising global temperatures. The research emphasized that without significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, these extreme weather events would become increasingly common, posing a persistent threat to communities worldwide. The study also highlighted the need for improved predictive models and early warning systems to better prepare for future storms.
The Devastating Effects of Severe Flooding in Central Europe
The flooding caused by Storm Boris led to unprecedented levels of destruction. Entire communities were submerged, with homes, businesses, and public facilities rendered unusable. Emergency services were overwhelmed, and the recovery process has been slow and arduous. The psychological toll on the affected populations has been immense, with many residents losing not only their homes but also their sense of security. The trauma of witnessing such widespread devastation has left deep emotional scars, particularly among children and the elderly. The loss of personal belongings, cherished memories, and the disruption of daily life have compounded the mental health crisis in the aftermath of the flooding. Community support systems have been crucial in providing emotional and psychological aid, but the road to recovery remains long and challenging. The social fabric of many towns and villages has been altered, with some residents choosing to relocate permanently due to the fear of future floods.
Climate Change and Flood Risk
The study underscores a troubling trend: as global temperatures rise, so does the risk of severe flooding. Warmer air holds more moisture, leading to more intense and frequent rainfall events. This is particularly concerning for regions like Central Europe, which are already prone to flooding due to their geographical and climatic conditions. The increased flood risk necessitates urgent action to mitigate climate change and adapt infrastructure to withstand future events. Urban planning and development strategies must incorporate flood resilience measures, such as improved drainage systems, flood barriers, and the restoration of natural floodplains. Additionally, public awareness campaigns are essential to educate communities about the risks and preparedness measures they can take. Governments and local authorities need to invest in sustainable practices and renewable energy sources to reduce the overall carbon footprint and slow the pace of global warming. Collaborative international efforts are also vital to address the global nature of climate change and its impacts.
Economic and Humanitarian Impact
The economic impact of the flooding has been staggering. The destruction of infrastructure, homes, and businesses has resulted in billions of euros in damages. In addition to the immediate costs of recovery and rebuilding, there are long-term economic consequences, including lost productivity and increased insurance premiums. On a humanitarian level, the floods have displaced thousands of people, leading to a crisis in temporary housing and basic needs. The displacement has strained social services and created challenges in providing adequate shelter, food, and medical care. The economic burden extends beyond the immediate aftermath, as businesses struggle to recover, and local economies face prolonged disruptions. The increased demand for construction materials and labor has driven up costs, further complicating the rebuilding efforts. Insurance companies are also grappling with the surge in claims, leading to higher premiums and reduced coverage options for flood-prone areas. This economic strain highlights the importance of proactive measures to mitigate the impact of future floods and build more resilient communities.
Environmental Consequences and Future Risks
The environmental impact of the flooding extends beyond immediate damage. Floodwaters have contaminated water supplies, spread pollutants, and disrupted ecosystems. The long-term ecological consequences could be severe, affecting biodiversity and natural habitats. Moreover, the study warns that if global warming continues unchecked, the frequency and intensity of such storms will increase, posing even greater risks to both human and natural systems. Contaminated floodwaters can lead to outbreaks of waterborne diseases, posing additional health risks to affected populations. The disruption of ecosystems can result in the loss of wildlife habitats and the decline of species that are unable to adapt to the changing conditions. The alteration of landscapes through erosion and sediment deposition can also have lasting effects on agriculture and land use. The study emphasizes the need for comprehensive environmental management strategies to address these challenges and protect natural resources. Restoration efforts, such as reforestation and wetland conservation, can help mitigate some of the environmental damage and enhance the resilience of ecosystems.
The findings of the study also warn about the future possibilities if global warming continues to rise. If global warming reaches 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, the likelihood of severe four-day storms would increase by 50%. These storms would also grow in intensity, further exacerbating the already dire situation. The potential for more frequent and severe storms underscores the urgency of global climate action. Policymakers must prioritize climate mitigation and adaptation strategies to safeguard communities and ecosystems. This includes international cooperation to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, investment in renewable energy, and the development of innovative technologies to address climate challenges. The study serves as a stark reminder of the tangible consequences of climate inaction and the need for immediate and sustained efforts to combat global warming.
Despite advanced preparation and early forecasting, the flooding caused by Storm Boris led to extensive damage, highlighting the costly consequences of climate change. In response to this disaster, the European Union has committed €10 billion in aid, indicating the significant economic toll of these climate-related occurrences. The allocation of funds aims to support recovery and rebuilding efforts, as well as to enhance future resilience against similar events. The financial commitment underscores the importance of solidarity and collective action in addressing the impacts of climate change. However, the scale of the damage also highlights the limitations of current preparedness measures and the need for continuous improvement in disaster response strategies. The aid package includes provisions for infrastructure repair, support for affected businesses, and assistance for displaced individuals. It also emphasizes the importance of investing in sustainable development practices to reduce future vulnerabilities.
The study, led by Joyce Kimutai of Imperial College London, found the “fingerprints of climate change” in the intense rainfall. Kimutai’s research indicates a clear link between the use of fossil fuels and the severity of weather events. She warns that if the planet warms to 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, storms like Boris will occur 50% more often and bring at least 5% more rain. This would lead to more devastating floods, posing a serious threat to people’s lives, environments, and economies. The research highlights the critical need for a global transition to cleaner energy sources and the reduction of carbon emissions. It also calls for increased investment in climate research to better understand and predict extreme weather patterns. Kimutai’s findings provide valuable insights for policymakers, emphasizing the urgency of implementing effective climate policies and promoting sustainable practices at all levels of society.
Human-caused climate change is not only a future threat – it is already causing significant meteorological changes and catastrophic events. The situation calls for an immediate and effective response to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow down global warming, in an attempt to mitigate its devastating consequences. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to adopt sustainable practices and reduce their carbon footprint. This includes transitioning to renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, and supporting conservation efforts. Public awareness and education are also crucial in fostering a culture of sustainability and encouraging collective action. The study’s findings serve as a powerful reminder of the urgent need for global cooperation and commitment to addressing the climate crisis. The path to a sustainable future requires bold and decisive actions to protect the planet and ensure a livable environment for future generations.
Science4Data is committed to cut through greenwashing and measure real impact. Join the journey to a sustainable future. Your actions matter.
How LLMs in Revolutionizing Content Marketing
Large Language Models (LLMs), a subset of artificial intelligence, are redefining the content marketing landscape. These advanced models can process and generate human-like text, enabling marketers to create highly personalized and engaging content. This blog delves into the four pivotal areas where LLMs are making a substantial impact: personalization, scalability, SEO optimization, and data-driven insights.
What are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are sophisticated AI systems trained on vast datasets to understand and generate human-like text. They leverage machine learning algorithms to predict and produce coherent and contextually relevant content. LLMs are capable of understanding complex language patterns, making them invaluable tools for content creation and marketing.
Benefits of Using LLMs in Content Marketing
The integration of LLMs in content marketing offers numerous benefits. These models enhance efficiency, allowing marketers to produce large volumes of high-quality content quickly. They also enable deeper personalization, ensuring content resonates with individual users. Additionally, LLMs provide valuable data-driven insights, helping marketers refine their strategies and optimize campaign performance.
Personalization
LLMs excel at generating tailored content based on user preferences. Personalization is crucial in content marketing as it enhances user engagement and satisfaction. By analyzing user data, LLMs can craft content that resonates with individual users, addressing their specific needs and interests. This level of customization not only boosts engagement but also fosters brand loyalty.
Detailed Paragraphs on Personalization:
Understanding User Preferences: LLMs utilize vast datasets to understand user behavior, preferences, and interests. By analyzing data from various sources such as browsing history, social media interactions, and past engagements, LLMs can predict what kind of content will resonate with each user. This predictive capability allows marketers to deliver highly relevant content, increasing the likelihood of user engagement.
Dynamic Content Generation: Unlike static content, dynamic content generated by LLMs can adapt in real-time based on user interactions. For instance, if a user frequently engages with articles about digital marketing, the LLM can prioritize and recommend similar content. This adaptability ensures that users receive content that aligns with their current interests, keeping them engaged and coming back for more.
Enhanced User Experience: Personalization extends beyond just content recommendations. LLMs can personalize entire user experiences, from email marketing campaigns to website content. By providing users with a seamless and relevant experience, marketers can build stronger connections with their audience, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Scalability
One of the standout features of LLMs is their ability to scale content production. Traditional content creation methods can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. However, LLMs can generate vast amounts of content quickly and efficiently, meeting the diverse needs of different audience segments. This scalability allows marketers to maintain a consistent and robust content pipeline, ensuring timely and relevant content delivery.
Detailed Paragraphs on Scalability:
Efficient Content Production: LLMs can generate high-quality content at a fraction of the time it takes human writers. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for large-scale marketing campaigns that require a significant volume of content. By automating content production, marketers can focus on strategy and creative aspects, while LLMs handle the heavy lifting of content creation.
Meeting Diverse Needs: Different audience segments have unique content needs. LLMs can cater to these diverse needs by producing customized content for various segments. Whether it’s creating blog posts, social media updates, or product descriptions, LLMs ensure that each piece of content is tailored to the target audience, enhancing the overall effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Consistent Quality: Maintaining consistency in content quality is a challenge for many marketers. LLMs address this challenge by producing content that adheres to predefined guidelines and standards. This consistency not only enhances the brand’s voice and messaging but also ensures that all content meets the desired quality benchmarks.
SEO Optimization
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a critical component of content marketing. LLMs can analyze keywords, trends, and search engine algorithms to create content optimized for search engine visibility. By incorporating relevant keywords and phrases, LLMs ensure that the content ranks higher in search engine results, driving organic traffic to websites. This optimization not only increases visibility but also enhances the overall effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Detailed Paragraphs on SEO Optimization:
Keyword Analysis: LLMs can analyze vast amounts of data to identify the most relevant keywords for a given topic. By understanding the search behavior of users, LLMs can incorporate these keywords into the content, ensuring that it aligns with what users are searching for. This alignment is crucial for improving search engine rankings and driving organic traffic.
Content Structuring: Search engines prioritize well-structured content that provides value to users. LLMs can generate content that is logically organized, with clear headings, subheadings, and bullet points. This structuring not only enhances readability but also makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index the content, further boosting its visibility.
Trend Analysis: SEO is a dynamic field, with trends and algorithms constantly evolving. LLMs can keep up with these changes by continuously analyzing search engine updates and trends. By staying up-to-date with the latest SEO practices, LLMs ensure that the content remains optimized and relevant, maintaining its competitive edge in search engine rankings.
Data-Driven Insights
LLMs provide valuable data-driven insights that help refine marketing strategies. By analyzing user behavior, engagement metrics, and content performance, LLMs offer actionable insights that guide marketers in optimizing their campaigns. These analytics enable marketers to understand what works and what doesn’t, allowing them to make data-informed decisions and improve content efficacy.
Detailed Paragraphs on Data-Driven Insights:
User Behavior Analysis: LLMs can analyze user interactions across various touchpoints to gain insights into their preferences and behavior. This analysis helps marketers understand which types of content resonate most with their audience, allowing them to tailor future content accordingly. By leveraging these insights, marketers can create more targeted and effective campaigns.
Performance Metrics: Measuring the performance of content is critical for optimizing marketing strategies. LLMs can track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and engagement metrics. By analyzing these metrics, LLMs provide a clear picture of how content is performing, enabling marketers to make data-driven decisions to improve their campaigns.
Strategy Refinement: Data-driven insights from LLMs can inform various aspects of marketing strategy, from content creation to distribution channels. By understanding what works and what doesn’t, marketers can refine their strategies to maximize impact. This continuous optimization ensures that marketing efforts are always aligned with audience preferences and industry trends.
Developing Effective Content Strategies
Developing effective content strategies involves understanding the target audience, setting clear objectives, and leveraging the capabilities of LLMs. By identifying the needs and preferences of the audience, marketers can create content that resonates and engages. Setting measurable goals ensures that content efforts are aligned with business objectives, while LLMs provide the tools to execute these strategies efficiently.
Leveraging LLMs for High-Quality Content Creation
Leveraging LLMs for high-quality content creation involves utilizing their advanced capabilities to produce engaging and relevant content. LLMs can generate content that is not only grammatically correct but also contextually appropriate. By incorporating LLMs into the content creation process, marketers can ensure that their content stands out in a crowded digital landscape.
Best Practices for Marketing and Content Creation with LLMs
To maximize the benefits of LLMs in marketing and content creation, it’s essential to follow best practices. These include continually updating LLMs with the latest data, ensuring content aligns with brand guidelines, and regularly monitoring content performance. Additionally, integrating human oversight ensures that the content remains authentic and resonates with the target audience.
LLMs are revolutionizing content marketing by offering enhanced personalization, scalability, SEO optimization, and data-driven insights. As these AI models continue to evolve, their impact on the marketing landscape will only grow, providing marketers with powerful tools to create compelling and effective content. Embracing LLMs in content marketing strategies is no longer a choice but a necessity for staying competitive in the digital age.
Content Gap Analysis
To ensure that your content remains relevant and engaging, conducting a content gap analysis is crucial. This process involves identifying areas where content is lacking or outdated and creating new content to fill these gaps. By regularly performing robust content gap analyses, marketers can stay ahead of trends and maintain a fresh and engaging content pipeline.
Successful Community Engagement Practices
Implementing successful community engagement practices can significantly enhance your brand’s online presence. By actively participating in online communities and sparking engaging forum discussions, marketers can build a loyal and active audience. Understanding audience interaction patterns and leveraging user-generated content ideas can further boost community engagement and brand loyalty.
Leveraging Past Successful Content
One effective strategy for content marketing is leveraging past successful content. By analyzing what has worked well in the past, marketers can identify patterns and replicate success. This approach not only saves time but also ensures that the content resonates with the target audience. Understanding past successful content and audience expectations can guide future content creation efforts.
Keyword Research and Content Optimization
Effective keyword research is essential for SEO optimization. By identifying not only popular keywords but also long-tail keywords, marketers can create content that ranks well in search engines. Additionally, content optimization involves structuring content in a way that enhances readability and search engine visibility. Regularly updating content based on current market trends and relevant industry trends ensures that it remains competitive.
Identifying Target Audiences
Understanding and identifying target audiences is fundamental to successful content marketing. By pinpointing the demographics, interests, and preferences of your audience, you can create content that resonates and engages. This targeted approach ensures that your marketing efforts are effective and aligned with audience needs.
Social Media Presence
Maintaining a strong social media presence is essential for modern content marketing. By staying active on social media platforms and keeping up with social media trends, marketers can reach a wider audience and drive engagement. Regularly updating social media content and interacting with followers helps build a loyal and engaged community.
Brand Voice and Creative Process
Establishing a consistent brand voice is crucial for building a strong brand identity. By ensuring that all content aligns with the brand’s tone and messaging, marketers can create a cohesive and recognizable brand image. Additionally, incorporating LLMs into the creative process can enhance content creation efforts, ensuring that the content is both engaging and contextually relevant.
Engagement and Conversion Rates
Monitoring engagement and conversion rates is essential for evaluating the success of content marketing efforts. By analyzing these metrics, marketers can understand what content resonates with the audience and drives conversions. This data-driven approach allows for continuous optimization and improvement of content strategies.
Online Community and Human Language
Building a strong online community involves understanding how to communicate effectively in human language. By creating content that is relatable and engaging, marketers can foster a sense of community and loyalty among their audience. Regularly interacting with the community and addressing their needs helps build trust and long-term relationships.
Pinpoint Relevant Industry Trends
Staying updated with relevant industry trends is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. By regularly analyzing and incorporating these trends into content creation efforts, marketers can ensure that their content remains relevant and engaging. This proactive approach helps brands stay ahead of the curve and maintain their position in the market.
LLMs are revolutionizing content marketing by offering enhanced personalization, scalability, SEO optimization, and data-driven insights. As these AI models continue to evolve, their impact on the marketing landscape will only grow, providing marketers with powerful tools to create compelling and effective content. Embracing LLMs in content marketing strategies is no longer a choice but a necessity for staying competitive in the digital age.
Multi-Agent Systems in Intelligent Energy Grids
Introduction to Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems (MAS) are computational systems in which multiple autonomous entities, known as agents, interact or work together to perform tasks or solve problems. Each agent in a MAS has its own capabilities, goals, and behavior, and can operate independently or collaboratively with other agents. In the context of smart grids, MAS are employed to improve the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of energy distribution and consumption.
MAS are designed to manage complex and dynamic environments, making them well-suited for the challenges presented by modern energy grids. These systems enable decentralized control, allowing for more flexible and adaptive management of energy resources. By leveraging the capabilities of MAS, smart grids can effectively integrate renewable energy sources, optimize energy distribution, and maintain a stable supply-demand balance.
Renewable Energy Integration
The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the energy grid presents both opportunities and challenges. Renewable energy is inherently variable and intermittent, which can lead to fluctuations in power generation and supply. MAS play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by providing a dynamic and adaptive framework for managing renewable energy resources.
In a smart grid, MAS can facilitate the seamless integration of renewable energy by coordinating the actions of various agents, such as energy producers, consumers, and storage systems. These agents can communicate and collaborate to optimize the use of renewable energy, minimize curtailment, and ensure a stable and reliable power supply. By leveraging the capabilities of MAS, smart grids can maximize the benefits of renewable energy while mitigating its inherent variability.
Energy Distribution Management
Efficient energy distribution is a critical component of a smart grid, and MAS are instrumental in achieving this goal. Traditional energy distribution systems rely on centralized control, which can be inflexible and slow to respond to changes in demand or supply. In contrast, MAS enable decentralized control, allowing for more responsive and adaptive management of energy distribution.
In a MAS-based smart grid, individual agents can monitor and manage different aspects of the energy distribution network, such as power lines, transformers, and substations. These agents can communicate with each other to share information and coordinate their actions, ensuring that energy is distributed efficiently and equitably. This decentralized approach enables the smart grid to quickly adapt to changes in demand or supply, reducing the risk of outages and improving overall reliability.
Real-Time Supply and Demand Balancing:
One of the primary challenges in managing an energy grid is maintaining a balance between supply and demand in real-time. MAS provide a powerful tool for achieving this balance by enabling dynamic and adaptive control of energy resources. In a MAS-based smart grid, agents can monitor real-time data on energy production, consumption, and storage, and use this information to make informed decisions about how to allocate resources.
For example, if a sudden increase in demand occurs, agents can quickly identify available energy sources and direct them to where they are needed most. Conversely, if there is an excess of energy supply, agents can coordinate actions to store or redistribute the surplus. This real-time balancing capability helps to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply, even in the face of fluctuations in demand or supply.
Sustainability in Energy Grids:
Sustainability is a key goal for modern energy grids, and MAS play a vital role in achieving this objective. By enabling more efficient and adaptive management of energy resources, MAS can help to reduce waste, minimize environmental impact, and promote the use of renewable energy sources.
In a MAS-based smart grid, agents can work together to optimize energy consumption, reduce peak demand, and improve overall efficiency. For example, agents can coordinate demand response programs, encouraging consumers to reduce their energy usage during peak times. Additionally, agents can manage energy storage systems, ensuring that renewable energy is stored and used effectively.
By leveraging the capabilities of MAS, smart grids can become more sustainable, resilient, and environmentally friendly. This not only benefits the environment but also helps to create a more reliable and cost-effective energy system for consumers.
Multi-agent systems (MAS) offer a powerful and flexible framework for managing the complexities of modern smart grids. By enabling decentralized control, dynamic resource allocation, and real-time balancing, MAS can help to integrate renewable energy sources, optimize energy distribution, and promote sustainability. As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, the role of MAS in smart grids will become increasingly important, paving the way for a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy future.
Connect with our expert to explore the capabilities of our latest addition, AI4Mind Chatbot. It’s transforming the social media landscape, creating fresh possibilities for businesses to engage in real-time, meaningful conversations with their audience
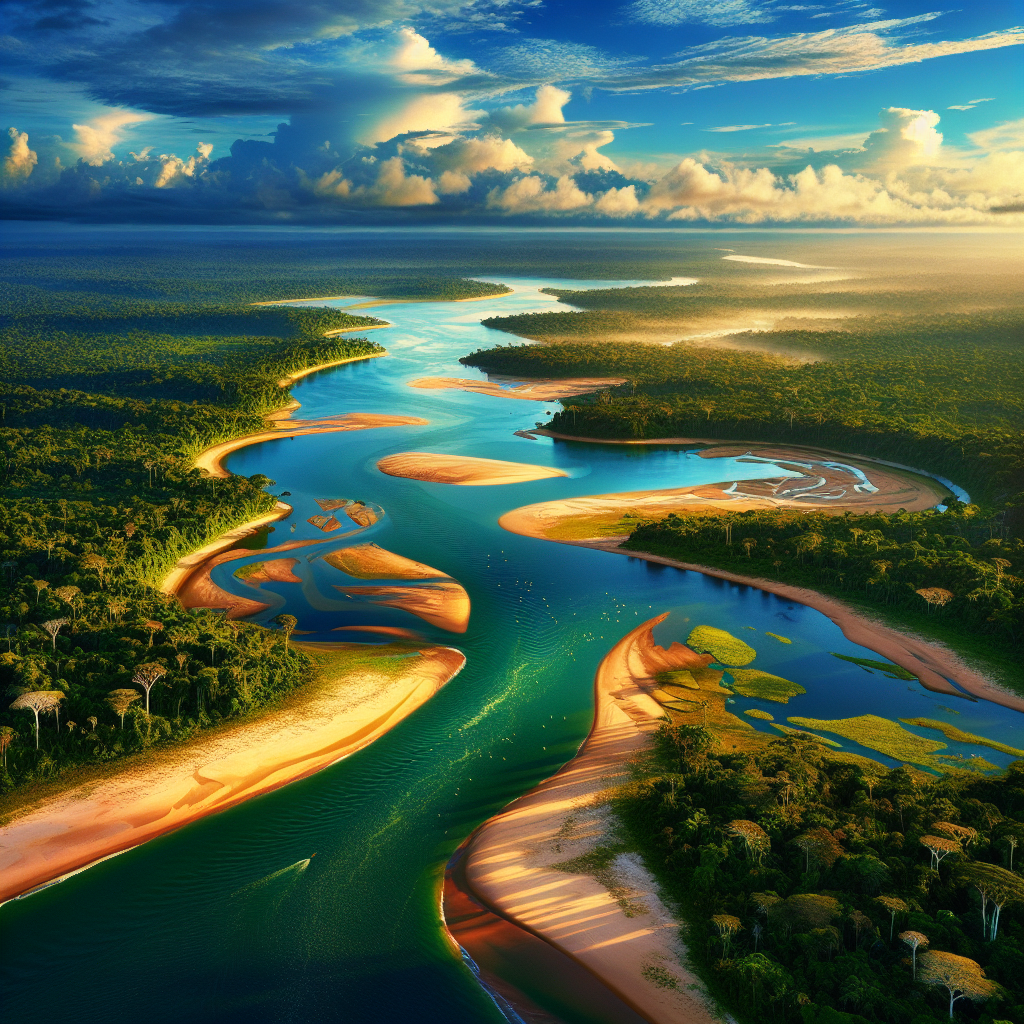
Greenpeace Activists Highlight Impact of Record-Breaking Drought on Vulnerable Communities
Greenpeace activists in Brazil have recently drawn attention to the record-breaking drought in the Amazon basin. Demonstrating their concern for the environmental catastrophe, the activists placed a banner on a newly formed sandbank in the basin’s major river, the Solimoes. The banner posed a simple yet profound question to the world: “Who Pays?”
The Amazon, often referred to as the ‘lungs of the Earth’, is currently grappling with an unprecedented drought, attributed to global warming and climate change. In particular, the continued use of fossil fuels is blamed for contributing significantly to the environmental damage in this region.
The intense drought has led to a drastic drop in the water level of the Solimoes River, exposing the riverbed and leaving communities that rely on the river for transport stranded. The situation is grave, with record-low water levels leading not just to wildfires and exposed riverbeds, but also to stranded river communities.
Romulo Batista, a spokesperson for Greenpeace Brazil, has highlighted the plight of vulnerable communities such as Indigenous people and fishermen, who are bearing the brunt of the effects of climate change in the Amazon. The drought has had severe consequences, including increasing river and lake water temperatures, which has led to the death of fish and endangered river dolphins.
Batista further asserts that climate change is already drying up the rivers in the world’s largest rainforest. According to him, water temperatures in the Solimoes River have skyrocketed, reaching a deadly 40 degrees Celsius. This increase in temperature is not just deadly for the aquatic life but also for the communities that depend on these water bodies for their livelihood.
Climate Change and the Amazon Basin Drought
Climate change is a significant factor contributing to the Amazon Basin drought. Rising global temperatures have altered weather patterns, leading to prolonged dry spells in regions that once enjoyed consistent rainfall. The Amazon’s unique ecosystem, which thrives on a delicate balance of wet and dry seasons, is being thrown into disarray. These changes exacerbate the vulnerability of the basin, making it more susceptible to severe drought conditions.
The Amazon rainforest, covering over 5.5 million square kilometers, is an intricate web of biodiversity that relies on consistent climatic conditions to sustain its flora and fauna. The alteration in weather patterns due to climate change disrupts this balance, leading to more frequent and intense droughts. These prolonged dry spells not only reduce the water availability in rivers and lakes but also increase the risk of wildfires, which can devastate large swathes of the forest. The reduced rainfall affects the soil moisture, making it harder for trees and plants to survive, further contributing to the degradation of the rainforest.
Agricultural Drought in South America
The agricultural sector in South America is also feeling the effects of the drought. Crops that depend on regular rainfall are suffering, leading to reduced yields and economic hardship for farmers. The lack of water affects not only the growth of crops but also the health of livestock. This agricultural drought has a ripple effect, impacting food security and the livelihoods of millions of people in the region.
Farmers in the Amazon basin and surrounding areas are experiencing unprecedented challenges as they struggle to maintain their agricultural practices amidst the severe drought. Staple crops such as maize, soybeans, and coffee are particularly vulnerable to changes in rainfall patterns. The reduced yields not only threaten the food supply but also lead to higher prices, making it difficult for low-income families to afford basic necessities. Livestock, which relies on a steady supply of water and forage, is also suffering, leading to decreased productivity and increased mortality rates. The economic impact on farmers is profound, with many facing financial ruin and being forced to abandon their land.
Ocean-Atmospheric Patterns and the Drought
Ocean-atmospheric patterns, such as El Niño and La Niña, play a crucial role in the Amazon Basin’s climate. These patterns can either bring excessive rainfall or prolonged dry periods. Recent shifts in these patterns have contributed to the current drought conditions. Understanding the interplay between oceanic changes and atmospheric conditions is essential for predicting and mitigating future droughts in the Amazon.
El Niño and La Niña are complex climate phenomena that significantly influence weather patterns around the globe. El Niño, characterized by the warming of ocean surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific, typically brings drier conditions to the Amazon basin. Conversely, La Niña, marked by cooler ocean temperatures, can lead to increased rainfall. However, the recent shifts in these patterns have become more erratic due to global warming, making it challenging to predict their impact accurately. The increased frequency and intensity of El Niño events have exacerbated the drought conditions in the Amazon, highlighting the need for comprehensive climate models to better understand and anticipate these changes.
Regional Rainfall Patterns and Global Warming
Global warming is altering regional rainfall patterns, leading to more erratic weather in the Amazon Basin. The once predictable wet and dry seasons are becoming increasingly irregular, making it difficult for the ecosystem and local communities to adapt. This shift not only affects water availability but also influences the overall health of the rainforest, which relies on consistent moisture levels to sustain its biodiversity.
The alteration in rainfall patterns due to global warming has far-reaching consequences for the Amazon basin. The irregularity in wet and dry seasons disrupts the natural cycles that many species depend on for survival. Plants and animals that have adapted to specific climatic conditions are struggling to cope with the changes, leading to a decline in biodiversity. The reduced water availability affects not only the aquatic ecosystems but also the terrestrial ones, as many species rely on the rivers and lakes for their water supply. The changing rainfall patterns also impact the carbon sequestration capacity of the rainforest, reducing its ability to absorb carbon dioxide and mitigate climate change.
Consequences for Local Ecosystems and Communities
The consequences of the drought for local ecosystems and communities are dire. Aquatic life, such as fish and freshwater dolphins, is particularly vulnerable to rising water temperatures and reduced water levels. The death of these species disrupts the food chain and affects the livelihoods of those who depend on fishing. Additionally, Indigenous communities, who have lived in harmony with the rainforest for generations, are facing unprecedented challenges as their traditional ways of life are threatened by the changing environment.
The rising water temperatures and reduced water levels in the Amazon basin have led to a significant decline in fish populations. Many species of fish are unable to survive in the warmer waters, leading to mass die-offs. This not only disrupts the aquatic food chain but also affects the livelihoods of local fishermen who rely on these fish for their income. The death of freshwater dolphins, which are already endangered, is particularly concerning as it indicates the severe impact of the drought on the ecosystem. Indigenous communities, who have a deep cultural and spiritual connection to the rainforest, are struggling to adapt to the changing environment. Their traditional knowledge and practices, which have been passed down through generations, are being rendered ineffective by the unprecedented changes brought about by climate change.
The question raised by Greenpeace’s banner remains relevant: “Who Pays?” As the world grapples with climate change and its disastrous effects, the cost is currently being paid by the ecosystem and the vulnerable communities that rely on it. It is a wake-up call for global leaders and policymakers to take immediate action to address the root cause of these environmental catastrophes, most notably, our continued dependency on fossil fuels. The Amazon crisis is not just a regional issue, but a global one that warrants urgent attention and action.
The international community must recognize the urgency of the situation and work together to implement sustainable solutions. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and protecting the remaining rainforest are critical steps that need to be taken. Additionally, supporting local communities in adapting to the changing environment and preserving their traditional knowledge is essential for ensuring their resilience in the face of climate change. The Amazon basin’s health is not only vital for the region but also for the entire planet, as it plays a crucial role in regulating the global climate and maintaining biodiversity.
Science4Data is committed to cut through greenwashing and measure real impact. Join the journey to a sustainable future. Your actions matter.
Climate Change Poster Collection of the Week – Fire Weather
This week’s Climate Change Poster Collection highlights Fire weather, a term used to describe meteorological conditions conducive to wildfires, is becoming increasingly frequent and intense due to the multifaceted impacts of climate change. High temperatures, prolonged droughts, and low humidity levels are the primary factors that create an environment ripe for wildfires, and these conditions are being exacerbated by the ongoing shifts in our global climate. As global temperatures continue to rise, heatwaves are becoming more common and severe, drying out vegetation and turning forests, grasslands, and shrublands into tinderboxes. The extended periods of high temperatures not only dry out the soil and vegetation but also reduce moisture levels in the air, creating conditions where even a small spark can ignite a massive blaze.
Climate change is also altering precipitation patterns, leading to longer dry spells and shorter, more intense bursts of rainfall, which fail to sufficiently hydrate the landscape. These shifts in weather patterns are exacerbated by human activities such as deforestation and land-use changes, which further increase the vulnerability of ecosystems to fire. Moreover, warmer temperatures and changing climate conditions are expanding the fire season, making it last longer and affecting regions that were previously less prone to wildfires. For instance, areas like the Arctic and boreal forests, which were once considered fire-resistant due to their cold climates, are now experiencing unprecedented wildfire activity.
The interplay between climate change and fire weather creates a vicious cycle: wildfires release large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which in turn contribute to further global warming. This feedback loop underscores the urgent need for comprehensive climate action to mitigate the factors driving these increasingly destructive wildfires. The economic and social impacts of wildfires are staggering, with billions of dollars in damages, loss of property, and the displacement of communities. The health impacts are also significant, as wildfire smoke can travel vast distances, affecting air quality and leading to respiratory issues and other health problems for people far removed from the fire’s origin.
Addressing fire weather requires a multifaceted approach, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, implementing better land management practices, and investing in early warning systems and firefighting resources. Forest management practices such as controlled burns and thinning can help reduce the amount of flammable material in forests, thereby lowering the risk of large, uncontrollable fires. Additionally, advances in technology, such as satellite monitoring and predictive modeling, can provide early warnings and help in the rapid deployment of firefighting resources.
Community preparedness is also crucial. Educating the public about fire safety, creating defensible spaces around properties, and developing evacuation plans can save lives and reduce the impact of wildfires. Governments and organizations must also invest in research to better understand the complex interactions between climate change and fire weather, enabling the development of more effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
As we grapple with the realities of a warming planet, understanding and mitigating the impacts of fire weather is crucial for protecting both natural ecosystems and human communities from the devastating effects of wildfires. The challenge is immense, but with coordinated global efforts and a commitment to sustainable practices, we can work towards a future where the risks of catastrophic wildfires are significantly reduced. The urgency of addressing fire weather cannot be overstated, as the window for effective action is narrowing with each passing year. By taking decisive steps now, we can help safeguard our planet and ensure a more resilient and sustainable future for generations to come.
Discover an inspiring collection of climate change poster.
480 Million Years of Climate – Insights and Imperatives for Our Future
A groundbreaking study led by Emily Judd at the University of Arizona and The Smithsonian takes a deep dive into the historical climate conditions of our planet. The researchers meticulously studied over 150,000 pieces of fossil evidence in conjunction with advanced climate models to determine Earth’s global surface temperatures over an expansive time scale of 480 million years. The revelations from this study are startling. They found that Earth has experienced significantly higher temperatures for the majority of the past 480 million years. However, it is the rate of the current temperature rise that is most alarming, as the planet has never experienced such a rapid escalation before.
During the majority of the Phanerozoic Eon, a geological period that spans over 541 million years, the average temperatures were above 71.6°F (22°C). This was a period characterized by little to no ice at the poles. On the other hand, humans evolved during the coldest epoch, when global average surface temperatures were as low as 51.8°F (11°C). This stark contrast highlights the variability in Earth’s climate over geological time scales and underscores the unique climatic conditions under which human civilization developed. Drawing from these historic temperature trends, the research suggests that if the current rate of greenhouse gas emissions continues unchecked, we could be looking at global temperatures nearing 62.6°F (17°C) by the end of this century.
While such a temperature increase might not render Earth uninhabitable, the study indicates that the human-caused warming could cause significant upheaval to ecosystems and communities worldwide. The potential consequences of global climate change, including more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and disruption to biodiversity, are cause for serious concern. The impact on agriculture, water resources, and human health could be profound, leading to food shortages, water scarcity, and increased incidence of heat-related illnesses. The research underscores the urgent need for a shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. Transitioning to cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions is crucial in order to mitigate the impacts of global warming.
Moreover, the study found that the climate sensitivity, defined as the extent of warming due to doubling of atmospheric carbon dioxide, has remained consistent across 485 million years. This holds true regardless of whether the climate was hot or cold, underscoring the detrimental impact of greenhouse gas carbon dioxide on our planet’s temperature. This consistency in climate sensitivity suggests that the basic mechanisms driving climate change are well-understood and predictable, providing a solid foundation for developing effective mitigation strategies. This comprehensive study, spanning hundreds of millions of years, serves as a stark reminder of the urgency of addressing global climate change. The findings underscore the critical need for swift action to curb carbon emissions and transition to clean, renewable energy sources.
Historical Temperature Changes
Over the course of Earth’s history, global temperatures have fluctuated dramatically. These changes have been driven by a variety of natural factors, including volcanic activity, variations in solar radiation, and shifts in the Earth’s orbit. By examining fossil records, scientists have been able to reconstruct past climate conditions, providing valuable insights into how our planet’s climate has evolved over millions of years. These historical temperature changes have had profound impacts on the development and extinction of species, the formation of ecosystems, and the distribution of life on Earth. Understanding these past climate conditions helps scientists make more accurate predictions about future climate trends and their potential impacts.
Factors Influencing Global Temperature
Several key factors influence global temperatures. These include greenhouse gases, solar radiation, volcanic activity, and ocean currents. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to warming. Volcanic eruptions can inject large quantities of ash and sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, temporarily cooling the planet. Changes in ocean currents can also redistribute heat around the globe, affecting regional climates. Additionally, human activities, such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, amplifying the natural greenhouse effect and accelerating global warming. The interplay of these factors creates a complex and dynamic climate system that is sensitive to both natural and human-induced changes.
Regional Temperature Variations
While global average temperatures provide a broad overview of climate change, regional variations can be quite pronounced. Different parts of the world experience warming or cooling at different rates due to factors such as geography, ocean currents, and atmospheric circulation patterns. For example, polar regions are warming much faster than the global average, leading to accelerated ice melt and rising sea levels. In contrast, some regions may experience little to no warming or even cooling due to localized factors such as ocean currents or volcanic activity. These regional variations can have significant implications for local ecosystems and human communities, influencing weather patterns, agricultural productivity, and water availability.
Implications of Global Temperature Changes
The implications of rising global temperatures are far-reaching and profound. Ecosystems are being disrupted, leading to shifts in species distributions and the potential for widespread extinctions. Coral reefs, which are highly sensitive to temperature changes, are experiencing widespread bleaching and die-offs. Human communities are also at risk, with increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and floods. Additionally, rising sea levels threaten coastal cities and infrastructure, potentially displacing millions of people. The economic costs of these impacts are substantial, affecting industries such as agriculture, fisheries, tourism, and real estate. The social and political consequences of climate change, including migration and conflict over resources, are also significant and require coordinated global responses.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
To address the challenges posed by global climate change, both mitigation and adaptation strategies are essential. Mitigation involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow the rate of warming. This can be achieved through transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and protecting forests. Renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, offer sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels and have the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions. Adaptation, on the other hand, involves making adjustments to social, economic, and environmental practices to minimize the damage caused by global climate change. This includes building resilient infrastructure, developing early warning systems for extreme weather events, and implementing sustainable agricultural practices. Urban planning and design can also play a crucial role in enhancing the resilience of cities to climate impacts, through measures such as green roofs, permeable pavements, and improved drainage systems. By combining mitigation and adaptation efforts, we can better prepare for and respond to the challenges of a changing climate, ensuring a more sustainable and resilient future for all.”
Science4Data is committed to cut through greenwashing and measure real impact. Join the journey to a sustainable future. Your actions matter.